This guide will help you get started with podcasting, which is like having your own radio show that people can listen to anytime! We'll cover everything from how to begin, what equipment you need, how to make your recordings sound great, and how to share your podcasts with others. By the end, you'll have all the basic knowledge you need to create your very own podcasts and share your amazing ideas with the world.



Vanessa Rodriguez
- Head, Creative Studio
- vrodrigu@miami.edu
- (305) 284-4042

Nicolas Aponte
- Emerging Technologies Librarian
- nickaponte@miami.edu
- (305) 284-2085
Before you start recording your podcast, think about what you want to talk about and how you want to talk about it. Do you want to script everything you say or just speak naturally? It's important to choose a topic that you really love and care about because that will make your podcast more interesting. Think about who you want listening to your podcast. What are they interested in? What do they like to hear? When you talk on your podcast, be yourself and be real! That way, people will feel like they know you and want to keep listening.


Here are some helpful links that provide more information on how to start making a podcast from the beginning.
- a How to Start a Podcast
Learn how to start a podcast, launch your show and start growing! This complete step-by-step beginners guide goes from initial idea, to going live, to snagging your first 100 listeners. - a Everything You Need to Know to Start a Podcast
A step-by-step guide to getting started in the world of podcasting.
To ensure a smooth podcast recording, create an outline. Here's a simplified process:
- Define purpose, topics, and target audience.
- Identify sections: intro, main content, interviews, conclusion.
- Research and gather accurate information.
- Organize main points logically.
- Add supporting subpoints or examples.
- Plan smooth transitions between segments.
- Include engaging elements like anecdotes or audio clips.
- Decide episode length.
- Revise and refine the outline for clarity.
- When ready, start recording your podcast episode.
Picking the right microphone for recording is super important to make sure your audio sounds awesome! There are three main types to choose from: condenser, dynamic, and USB microphones.
Condenser microphones need special power called phantom power, which comes from audio interfaces. They capture all the little details and make your sound super clear. They're great for recording in a studio.
Dynamic microphones have a warm sound and don't need phantom power. They're really tough and can handle loud sounds. People often use them for live performances.
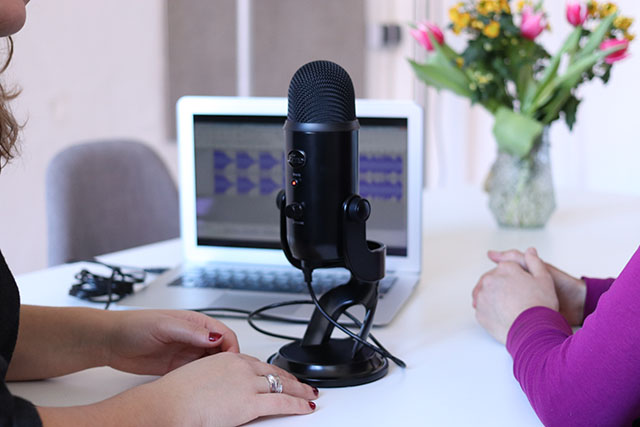
USB microphones are really easy to use and don't need extra equipment. You just plug them into your computer and you're ready to record! They're perfect for podcasting and if you're just starting out.
Each type of microphone has its own benefits, so it depends on things like where you're recording, what you're recording for, and what kind of sound you like. It's all about finding the microphone that works best for you!
Condenser microphones need special power called phantom power, which comes from audio interfaces. They capture all the little details and make your sound super clear. They're great for recording in a studio.
Dynamic microphones have a warm sound and don't need phantom power. They're really tough and can handle loud sounds. People often use them for live performances.
USB microphones are really easy to use and don't need extra equipment. You just plug them into your computer and you're ready to record! They're perfect for podcasting and if you're just starting out.
Each type of microphone has its own benefits, so it depends on things like where you're recording, what you're recording for, and what kind of sound you like. It's all about finding the microphone that works best for you!
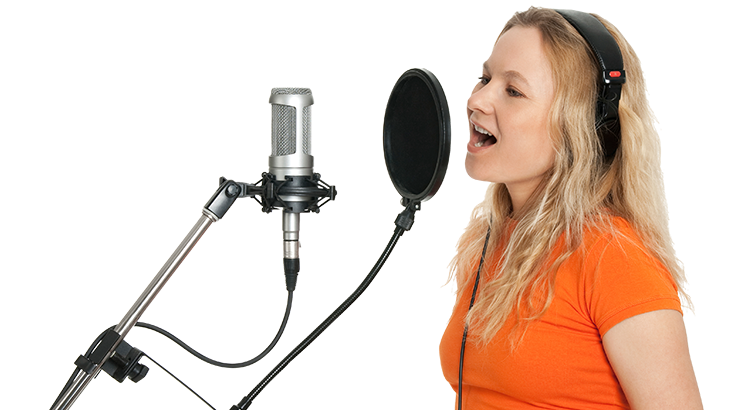
When you're speaking into a microphone, it's important to prevent unwanted plosive sounds. Plosives happen when a strong burst of air hits the microphone, usually when you emphasize "b" or "p" sounds in certain words. To avoid this, you can position the microphone about 45 degrees to the side of your mouth, so the plosives don't go directly into it. Another solution is to use a pop filter, which helps reduce or even eliminate popping sounds caused by fast-moving air hitting the microphone during speech or singing.


- Creative Studio Music Equipment Catalog
As a University of Miami patron, you can borrow audio equipment from the music library for free. Simply reserve the equipment you need online and once you receive confirmation, you can pick it up at the library. - Creative Studio Audio Production Booth Reservation
The Audio Production Booths are located on the second floor of the music library. They are available on weekdays during two time blocks: from 9am to 12pm and 1:30pm to 4:30pm. As a University of Miami patron, you can reserve these booths and use them for various audio production projects, including music composition or podcast recording.
When you using a condenser or dynamic microphone, you need something called an audio interface to connect it to your computer. The audio interface acts like a translator, changing the microphone's sound into a language the computer can understand.
To connect the microphone to the audio interface, you use a special cable called an XLR cable. If you have more than one microphone, you need an audio interface with extra spots for the cables. Once everything is connected, you use a USB cable to connect the audio interface to your computer.
The audio interface lets you control how loud the microphone is, so you can make sure it sounds just right. It's important to find the right balance, not too loud or too quiet.
To connect the microphone to the audio interface, you use a special cable called an XLR cable. If you have more than one microphone, you need an audio interface with extra spots for the cables. Once everything is connected, you use a USB cable to connect the audio interface to your computer.

The audio interface lets you control how loud the microphone is, so you can make sure it sounds just right. It's important to find the right balance, not too loud or too quiet.
When recording a podcast, it's important to pay attention to the acoustics of your recording space. Acoustical treatment helps create the best sound environment by reducing echoes, reverberations, and unwanted noises. It makes your audio recordings clearer and more enjoyable for listeners. Acoustical treatment can involve using special materials like foam panels and bass traps to absorb sound. By taking care of the acoustics, you can make sure your podcast sounds professional and has great audio quality.
- Free Ways to Reduce Echo for Better Sound Quality and Recording
- This video explores ways to improve the acoustical treatment using materials commonly found around the house such as pillows and blankets.
- Do You Need Soundproofing For Your Podcast?
- This video offers a different perspective on the need for soundproofing.
Editing is a crucial step in creating a high-quality podcast. It's like fine-tuning your recorded audio to make it sound its best. Once you've recorded your podcast episode, you'll use editing software like Audition, Audacity or GarageBand to enhance the sound. You can remove any mistakes or awkward pauses, adjust volume levels, and add background music or sound effects to make it more engaging. Editing allows you to create a smooth and professional final product that your listeners can enjoy.
- Adobe Creative Cloud
Adobe Creative Cloud (CC) is available at no cost to all active University of Miami faculty, staff, and students. Adobe CC gives you access to a collection of Adobe applications for Graphic Design, Video Editing, Web Development, Photography, and Cloud Services. With Adobe CC, there's something for everyone, and you don't have to be an expert to use it! - Audacity
Audacity is a free, easy-to-use, multi-track audio editor and recorder for Windows, macOS, GNU/Linux and other operating systems.
Removing Mistakes: Use the editing software to cut out any mistakes, like stumbles or incorrect information. It helps make your podcast sound polished and professional.
Trimming Silence: Edit out long pauses or awkward silences to keep the pacing of your podcast smooth and engaging.
Adjusting Volume Levels: Ensure consistent audio levels throughout your episode. Increase the volume if something is too quiet or decrease it if it's too loud. This helps maintain a balanced listening experience.
Adding Music and Sound Effects: Spice up your podcast by incorporating background music or sound effects. They can set the mood, emphasize important points, or transition between segments.
Mixing and Fading: Blend different audio elements together by adjusting their levels. Use fading techniques to smoothly transition between music, segments, or guest interviews.
Exporting and Saving: After editing, export your podcast episode into a format that's suitable for sharing, such as MP3. Save your edited files with clear and organized names for easy access in the future.
Trimming Silence: Edit out long pauses or awkward silences to keep the pacing of your podcast smooth and engaging.
Adjusting Volume Levels: Ensure consistent audio levels throughout your episode. Increase the volume if something is too quiet or decrease it if it's too loud. This helps maintain a balanced listening experience.
Adding Music and Sound Effects: Spice up your podcast by incorporating background music or sound effects. They can set the mood, emphasize important points, or transition between segments.
Mixing and Fading: Blend different audio elements together by adjusting their levels. Use fading techniques to smoothly transition between music, segments, or guest interviews.
Exporting and Saving: After editing, export your podcast episode into a format that's suitable for sharing, such as MP3. Save your edited files with clear and organized names for easy access in the future.
File Management: Keeping track of your files is vital for easy access, consistency, collaboration, and protection. It saves time, maintains professionalism, enables smooth workflow, and safeguards your work. Stay organized to find files quickly and avoid errors or losses.
Shortcut Keys: Learning shortcut keys in podcast production can help you edit faster and more efficiently. With just a few key presses, you can cut, paste, adjust volume, and perform editing tricks like a pro. It saves time and boosts your podcasting skills.
Saving Backups: Saving backups in podcast production is like having a safety net. It protects your hard work from unexpected disasters, like computer crashes or accidental file deletion. Backups ensure you never lose your podcast episodes, scripts, or valuable edits. It's like having a spare copy that you can rely on when things go wrong.
Developing a Workflow: Developing a workflow helps you stay organized and efficient throughout the process. From recording to editing and publishing, a workflow guides your steps, ensuring tasks are completed in the right order. It saves time, reduces stress, and helps you create high-quality podcasts with ease.
Shortcut Keys: Learning shortcut keys in podcast production can help you edit faster and more efficiently. With just a few key presses, you can cut, paste, adjust volume, and perform editing tricks like a pro. It saves time and boosts your podcasting skills.
Saving Backups: Saving backups in podcast production is like having a safety net. It protects your hard work from unexpected disasters, like computer crashes or accidental file deletion. Backups ensure you never lose your podcast episodes, scripts, or valuable edits. It's like having a spare copy that you can rely on when things go wrong.
Developing a Workflow: Developing a workflow helps you stay organized and efficient throughout the process. From recording to editing and publishing, a workflow guides your steps, ensuring tasks are completed in the right order. It saves time, reduces stress, and helps you create high-quality podcasts with ease.
Other Software Editing Tutorials
- Audacity: Completely free, open sourced audio software that is compatible with both Mac and PC. Audacity has a moderate learning curve and the user interface is extremely dated, however, there are many tutorials online on how to use it and it is more than capable to produce professional sounding podcast productions.
- GarageBand: GarageBand is a software exclusively available on Mac computers. It comes pre-installed and is beginner-friendly, making it easy to learn. With its wide range of features, GarageBand is a great choice for audio production.
- Pixabay: Pixabay is a free stock photography and royalty-free stock media website. It is used for sharing photos, illustrations, vector graphics, film footage, music and sound effects, exclusively under the custom Pixabay license, which generally allows the free use of the material with some restrictions.
- Chosic: Chosic is a music library with downloadable music files free to use for commercial and non-commercial purposes.
- YouTube Studio: YouTube Studio is a platform provided by YouTube. By logging in, you can access YouTube Studio's Audio Library which will give you downloadable access to royalty free music and sound effects.
- Freesound: Freesound is a collaborative database of Creative Commons Licensed sounds. Browse, download and share sounds.
- Adobe Podcast Enhance
Adobe's speech enhancement platform that makes voice recordings sound as if they were recorded in a professional studio.
Podcast hosting platforms have important responsibilities when it comes to hosting and distributing your podcast. They provide secure storage for your audio files and generate an RSS feed, which is a special file that contains information about your episodes. This feed is used to distribute your podcast to popular platforms like Apple Podcasts and Spotify. Hosting platforms also offer analytics, giving you insights into your podcast's performance and audience. Customization options allow you to create a podcast website and personalize your podcast player. Some platforms even offer monetization options to help you generate revenue. Additionally, they provide technical support and handle the maintenance of their hosting infrastructure, freeing you up to focus on creating content.
Here is a simplified process for considering a podcast hosting platform:
Here is a simplified process for considering a podcast hosting platform:
- Research: Explore different hosting platforms and compare their features, pricing, and user reviews.
- Consider your needs: Think about the size of your podcast, expected audience, storage requirements, analytics, and monetization options.
- Evaluate platform features: Look for essential features like RSS feed generation, episode management, customizable player, distribution to major podcast directories, and podcast website support.
- Pricing: Compare pricing plans and consider your budget, including any additional costs for storage or bandwidth.
- User-friendly interface: Ensure the platform has an intuitive and easy-to-use interface for uploading, scheduling episodes, and managing your podcast.
- Support and resources: Check if the platform offers reliable customer support and provides resources like tutorials or a knowledge base.
- Make a decision: Based on your research and considerations, choose the podcast hosting platform that best fits your needs and budget.
Promoting Your Podcast:
- Utilize social media platforms to share episode releases, behind-the-scenes content, and engage with your audience.
- Collaborate with other podcasters, influencers, or relevant communities for cross-promotion opportunities.
- Consider creating a dedicated podcast website or blog to showcase your episodes and provide additional resources.
- Encourage listeners to leave reviews and ratings on podcast platforms.
- Respond to comments, questions, messages, and feedback from your audience.
- Consider hosting Q&A sessions, interviews, or listener contests to foster community engagement.